Glycerin
- also known as
- glycerine
- glycerol
- the backbone of
- triglycerides
- phospholipids
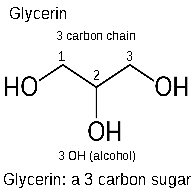
-// Construction to show graphic
a 3 carbon sugar backbone
- Each of the 3 carbons can attach to other molecules
- If all three carbons attach to a fatty acid it is a triblyceride
-\\
Fatty acid
example
Triglyceride
- 3 glycerol carbons attached to 3 separate fatty acids
- Triglycerides are independent from further attachments
- Independent triglycerides freely float through blood and tissues to cause harm
Phospholipid
- composed of a 3 carbon glycerol, 2 fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a polar molecule
- A phospholipids is an enhanced triglycerides
- triglycerides are stand alone
- phospholipids are intertwined in membranes
Serine
- a 3 carbon amino acid, similar to glycerol
- Each of the 3 carbons can attach to other molecules
Sphingomyelin
- serine replaces the glycerol as the backbone 3 carbon chain
- critical component of myelin sheaths around nerves
- myelin allows nerves to side ways communicate
- essential for thought
- opposed to sensory nerves that cannot 'think'
Review
- segment backbones of 3 carbon chains, either
- glycerol, sugar
- serine, amine
- triglycerides are independent
- glycerol backbone
- 3 fatty acids
- phospholipids
one fatty acid, is replaced with a phospho group
complex and interconnect
- 2 types of phospholipids
- glycerol backbone,
- sugar
- phospholipid
- cell wall
- membranes
- serine backbone,
- amino acid
- sphingomyelin
- myelin sheaths
- nerve membranes
- both types expand larger than a triglyceride through phosphorus bonding
membranes
Cell walls
The phospholipids are important components of all cell membranes, internal and external.
The lipid that forms the framework of the cell membrane are phospholipids.
--------- for a definition page
The ratio of hydrogen and oxygen are always the same as water in a carbohydrate.
In a lipid the hydrogen to oxygen ratios are not the same as water, hydrate as in carbohydrate.
------