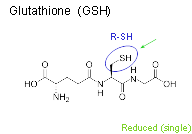
Forms of glutathione
- GSH - Glutathione, reduced, G-SH, Sulfur+Hydrogen
- GSSG - Gutathione disulfide, glutathione bound to itself, non-reactive
- GSNO - Nitrosglutathione , G-S-NO, Sulfur+Nitric Oxide
Glutathione
Nitrosglutathione (GSSG)
<image to come>
S-Nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) is an endogenous S-nitrosothiol (SNO) that plays a critical role in nitric oxide (NO) signaling and is a source of bioavailable NO.
GSNO in Health and Disease
GSNO and NO concentrations regulate respiratory function by modulating airway tone and pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in the respiratory tract.[14][15] Because NO is a labile gas and endogenous levels are difficult to manipulate, it has been proposed that exogenous GSNO could be used to regulate circulating levels of NO and NO-derived species, and GSNO could have value in patients with pulmonary diseases such as cystic fibrosis. Consistent with this therapeutic goal, a recent study showed that acute treatment with aerosolized GSNO was well tolerated by cystic fibrosis patients.[14]
SNOs in the hepatic mitochondria appear to influence proper functioning of the liver.
---------- disulfide
chemistry
- R−S−S−R′
- SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge
- usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups
biology,
- R-S-S-R
- thiol means sulfur
- cysteine is a single SH, (sulfur hydroxyl)
- disulfide, two cysteine residues
- important in structure of proteins
- persulfide, R−S−S−H compounds, note Hydrogen at the end